
For decades, the Earth’s ozone layer, which protects life on our planet from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays, has suffered from common chemicals used in everything from refrigerants to hairspray. But the ozone hole is now shrinking thanks to decades of global efforts to restore it, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) confirmed yesterday.

Ozone holes
The ozone hole is the thinning of the ozone layer in the stratosphere (the upper layer of the Earth’s atmosphere). For the first time, scientists discovered a hole in the ozone layer with a diameter of 1000 km over Antarctica in 1985. It appeared in autumn, and ceased its existence in December and January.
Over the Northern Hemisphere in the Arctic, numerous ozone mini-holes with an area of 2 million km² appear in autumn and winter, and the time of existence lasts up to a week.
The largest hole in Antarctica reached its maximum area in autumn 2021 (24.8 million km² – about the size of North America) before it began to shrink in mid-October.
Measurement of destruction
NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) researchers detect and measure the size of ozone holes using satellites and weather probes.
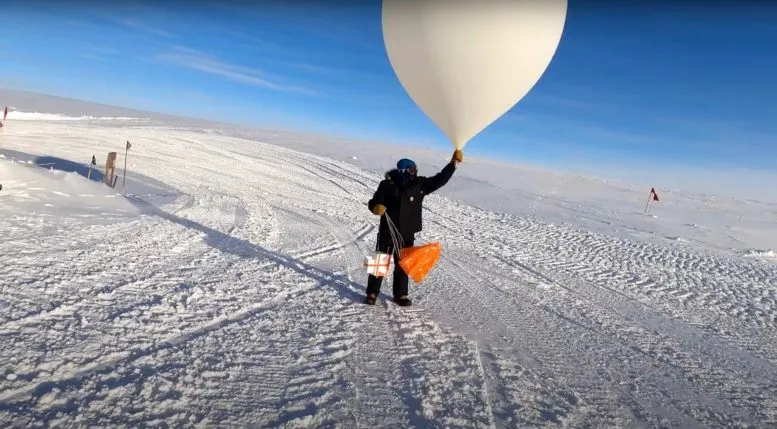

When the polar sun rises, NOAA scientists also measure with the Dobsonian spectrophotometer, an optical instrument that records the total amount of ozone between the surface and the edge of space.
In 2021, scientists recorded the lowest value of total ozone content, which was 102 Dobson units, the 8 lowest value since 1986. At altitudes from 14 to 21 kilometers, ozone was almost completely absent with the maximum increase of the ozone hole.
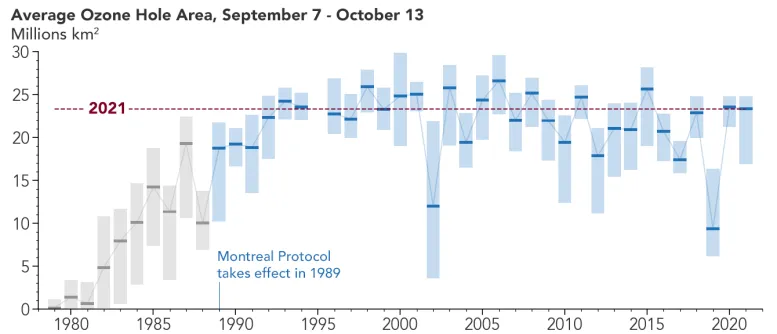
Despite this, the 2021 Antarctic ozone hole is significantly smaller than the holes of the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Montreal Protocol
In January 1989, the Montreal Protocol entered into force – the document and its subsequent amendments prohibited the emission of harmful substances that contribute to the destruction of the ozone layer.
If the amount of chlorine in the atmosphere this year were identical to the beginning of the 2000s, the ozone hole would be larger by about 4 million km² under the same weather conditions.
A panel of UN experts presented new forecasts at the annual meeting of the American Meteorological Society. It is expected that the ozone layer will be “healed” in the coming decades due to emission restrictions. By about 2066, the WMO estimates it will return to 1980 levels over Antarctica—before the holes appeared.
Because ozone depletion was the most severe there, other areas are expected to recover more quickly.
- In the north over the Arctic, by 2045 the ozone layer should look like it did in 1980.
- For the rest of the world, such recovery is expected by 2040.
The main offenders
Ozone molecules in the stratosphere absorb the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing much of it from reaching us. The process of formation and destruction of ozone in our atmosphere is constant, but certain chemicals can cause a disturbance in the balance – and then the destruction will be observed more often.
Among the harmful substances that affect the increase in holes, the following can be distinguished:
- chlorofluorocarbons – substances that were once used in refrigeration units, air conditioners, aerosol sprays and many other products.
- hydrochlorofluorocarbons – developed as less powerful substitutes for previous substances that still destroy the ozone layer.
Fortunately, today the Montreal Protocol has succeeded in phasing out approximately 99% of ozone-depleting substances.
Ozone-depleting reagents were later replaced by hydrofluorocarbons, which have been shown to be potent greenhouse gases. In 2016, the Kigali Amendment was added to the Montreal Protocol, which was supposed to limit the use of substances that heat the planet. These actions are expected to reduce global warming to 0.5°C by 2100.
*For context, the world has already warmed by about 1.2°C since the pre-industrial era — exacerbating many of the extreme weather events we live with today.
Abnormally warm winter in Europe: ski resorts are empty, gardens are blooming in the Czech Republic, and Kyiv sets temperature records for the third day in a row
Course
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS

Geoengineering
But there is a warning in the good news of the WMO. A panel of experts says that “geoengineering” — the deliberate manipulation of the climate and/or atmosphere to reverse some of the damage caused by burning fossil fuels — could potentially affect the ozone layer. They are particularly concerned about the stratospheric sulfur dioxide aerosol injection (SAI) tactic.
Proponents of the tactic believe it could cool the planet because the aerosols would reflect some of the sunlight back into space (an idea inspired by the cooling effects that typically follow large-scale volcanic eruptions). But according to a recent report supported by the World Health Organization, SAI “carries significant risks and may cause unintended consequences.”
Some climate experts are also concerned about a startup’s recent attempt to launch particles that reflect sunlight into the stratosphere.
Start-up Make Sunsets sprayed sulfur dioxide in the stratosphere to stabilize the climate and sells “credits” for the controversial technology – $10/gram
The US has now launched a 5-year research plan to examine all possible, albeit controversial, ways to mitigate global warming (including stratospheric aerosol spraying, sea lightening and cirrus cloud thinning).
Still, the phasing out of ozone-depleting chemicals is seen as an example of what humans can achieve by working together to solve the global environmental crisis.
“Our success in phasing out ozone-depleting chemicals shows what can and must be done – urgently – to move away from fossil fuels, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and thus lower temperatures,” WMO Secretary-General Petteri Taolas said in a statement. . .
Source: WMO, The Verge, Scitechdaily




