Russian APT groups, especially Sandworm, used threats to destroy data.

ESET, a leader in information security, has prepared an overview of cyberattacks on users using malware to destroy data before and after Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Most of these attacks can be attributed to the activities of the Sandworm cybercriminal group, which was previously known for its attacks on organizations in Ukraine.
In particular, after the Russian invasion, attackers became much more active in using threats to destroy data, targeting government institutions, banks, news agencies, logistics and energy companies in Ukraine. At the same time, a large number of attacks were detected and stopped in time.
Attacks on Ukrainian organizations before the invasion
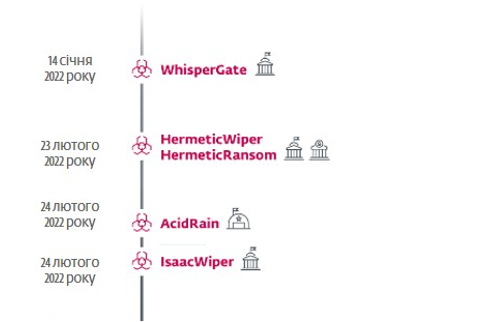
Prior to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, in addition to multiple waves of DDoS attacks, Ukrainian institutions were targeted by the WhisperGate malware on January 14, 2022. The data destruction threat masqueraded as ransomware, similar to NotPetya in 2017, a tactic that will also be seen in subsequent attacks.
Ahead of the February 23, 2022 invasion, at least five Ukrainian organizations were targeted by another HermeticWiper data destruction program. The cyber attack happened just hours before the invasion. In addition to HermeticWiper, the HermeticWizard worm and the HermeticRansom fake ransomware were also used at the time.
A new wave of cyber attacks during the invasion and in the first months of the war
On February 24, 2022, the second devastating attack on the Ukrainian government network using the program for data destruction – IsaacWiper – began. Viasat KA-SAT modems were targeted by another destructive threat, AcidRain, which spread beyond the borders of Ukraine.
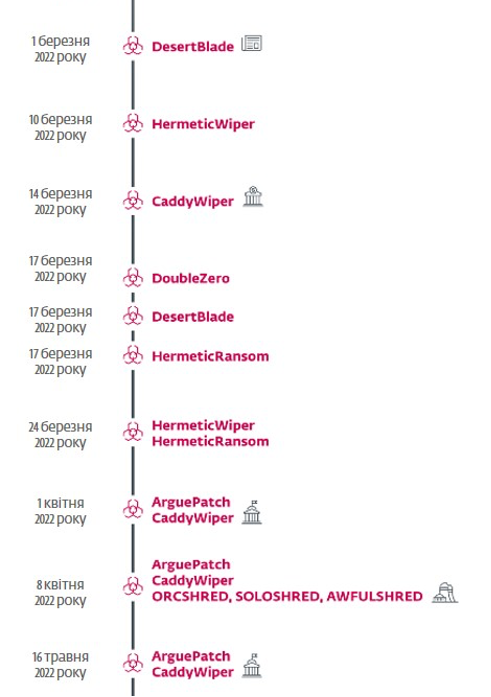
Another program with such functionality that Microsoft has discovered is DesertBlade, launched on March 1 and again around March 17, 2022. The report also mentions 3 more attacks using the previously mentioned HermeticWiper and HermeticRansom during March. On March 17, CERT-UA reported another data destruction program called DoubleZero.
At the same time, on March 14, ESET researchers discovered an attack using CaddyWiper aimed at a Ukrainian bank. Already at the beginning of April, this threat was discovered again. This time it was distributed using the ArguePatch loader, which is a modified legitimate binary used to load shellcode from an external file. ESET experts discovered a similar scenario on May 16, 2022, where ArguePatch took the form of a modified ESET binary.
ESET researchers also discovered the shared use of ArguePatch and CaddyWiper on April 8 in what is likely the Sandworm cybercriminal group’s largest attacks since the intrusion began. The attackers then failed in their attempt to shut down the power supply using the Industroyer2 malware.
Relatively quiet summer
Fewer new data destruction programs were discovered in Ukraine during the summer months compared to previous periods, but several notable attacks did occur.
ESET specialists together with CERT-UA worked on cases of deployment of the previously mentioned ArguePatch downloader and CaddyWiper program to destroy data in the networks of Ukrainian institutions. The incidents took place on June 20 and 23.

A new wave of malware spread in the fall
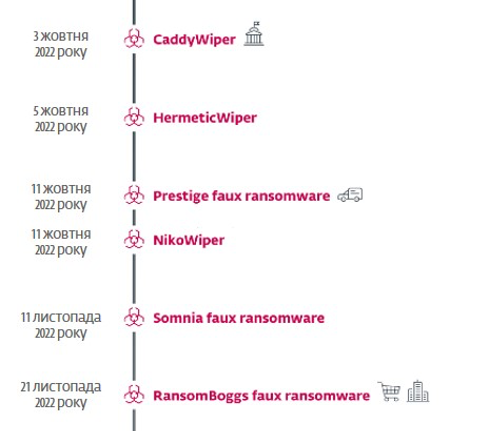
On October 3, 2022, ESET specialists discovered a new version of the CaddyWiper data destruction program in Ukraine. Unlike the previously used variants, this time CaddyWiper was compiled as an x64 Windows binary.
On October 5, a new version of HermeticWiper was uploaded to the VirusTotal resource. The functionality of this HermeticWiper sample was the same as previous versions, with a few minor changes.
On October 11, the new Prestige ransomware targeted logistics companies in Ukraine and Poland. On the same day, a previously unknown program for data destruction – NikoWiper – was discovered. This threat was aimed at a company in the energy sector of Ukraine. NikoWiper is based on Microsoft’s SDelete command-line utility for secure file deletion.
In early November, CERT-UA published material about an attack using the fake Somia ransomware. In the second half of the month, ESET specialists discovered a new RansomBoggs ransomware in Ukraine, written on the .NET platform. The threat contained several references to the movie Monsters Inc. Attackers used POWERGAP scripts to deploy ransomware.
First month of 2023: Attacks continue
In the new year, attacks on Ukrainian organizations continue. In particular, as early as January 1, ESET specialists detected the launch of the SDelete utility, which was targeted at Ukrainian software resellers.
Another attack using several data destruction programs, this time on a Ukrainian news agency, took place on January 17, 2023, according to CERT-UA. The following data-shredding programs were discovered during this attack: CaddyWiper, ZeroWipe, SDelete, AwfulShred, and BidSwipe, with the latter targeting the FreeBSD operating system.
On January 25, ESET specialists discovered a new data destruction program written in Go and called SwiftSlicer, which was targeting Ukrainian local self-government institutions.
In almost all of the above cases, the Sandworm cybercriminal group used Active Directory Group Policy to deploy its data destruction and ransomware threats, including using the POWERGAP script.

Result
Russian APT groups, especially Sandworm, have used data destruction threats, including those disguised as ransomware, to attack Ukrainian organizations and up to full-scale intrusions. Since around 2014, the BlackEnergy malware has been using plug-ins with data deletion functionality, and the data destruction program KillDisk has often been used by Sandworm in the past. In addition, the Telebots cybercriminal sub-group has carried out numerous ransomware attacks, the most famous of which is NotPetya.
However, the increased use of such threats since the full-scale invasion of February 2022 was unprecedented. It should be noted that many attacks have been detected and stopped. ESET specialists continue to monitor the situation in cyberspace in order to protect organizations and respond to cyber security incidents in a timely manner, as further attacks are likely to continue.
It should be noted that ESET research centers work around the clock to ensure comprehensive protection of users. In particular, during the year, ESET specialists repeatedly actively helped in the detection and investigation of cyber incidents aimed at Ukrainian organizations and users.
In addition, in addition to previously allocated funds, ESET will provide Ukraine with assistance in the amount of 500,000 euros. At the same time, 200,000 euros from this amount will be transferred to the Integra fund to provide urgent humanitarian aid to Ukraine.
Certificate. ESET is an expert in the field of protection against cybercrime and digital threats, an international developer of IT security solutions, a leading supplier in the field of creating threat detection technologies. Founded in 1992, ESET today has an extensive partner network and representative offices in more than 180 countries around the world. The company’s head office is located in Bratislava, Slovakia.





