The James Webb Telescope, which began operating last year, is giving us sharper images of celestial objects, revealing their hidden features, and looks like it could completely change our understanding of the cosmos today. By examining Webb’s images taken near the Big Dipper, scientists discovered 6 potential galaxies that probably formed 500-700 million years after the Big Bang.
But what makes them amazing is not their respectable age, but the number of stars. According to current cosmological theory, they simply shouldn’t exist—because there wasn’t enough matter back then for galaxies to form as many stars as there are in our Milky Way today.
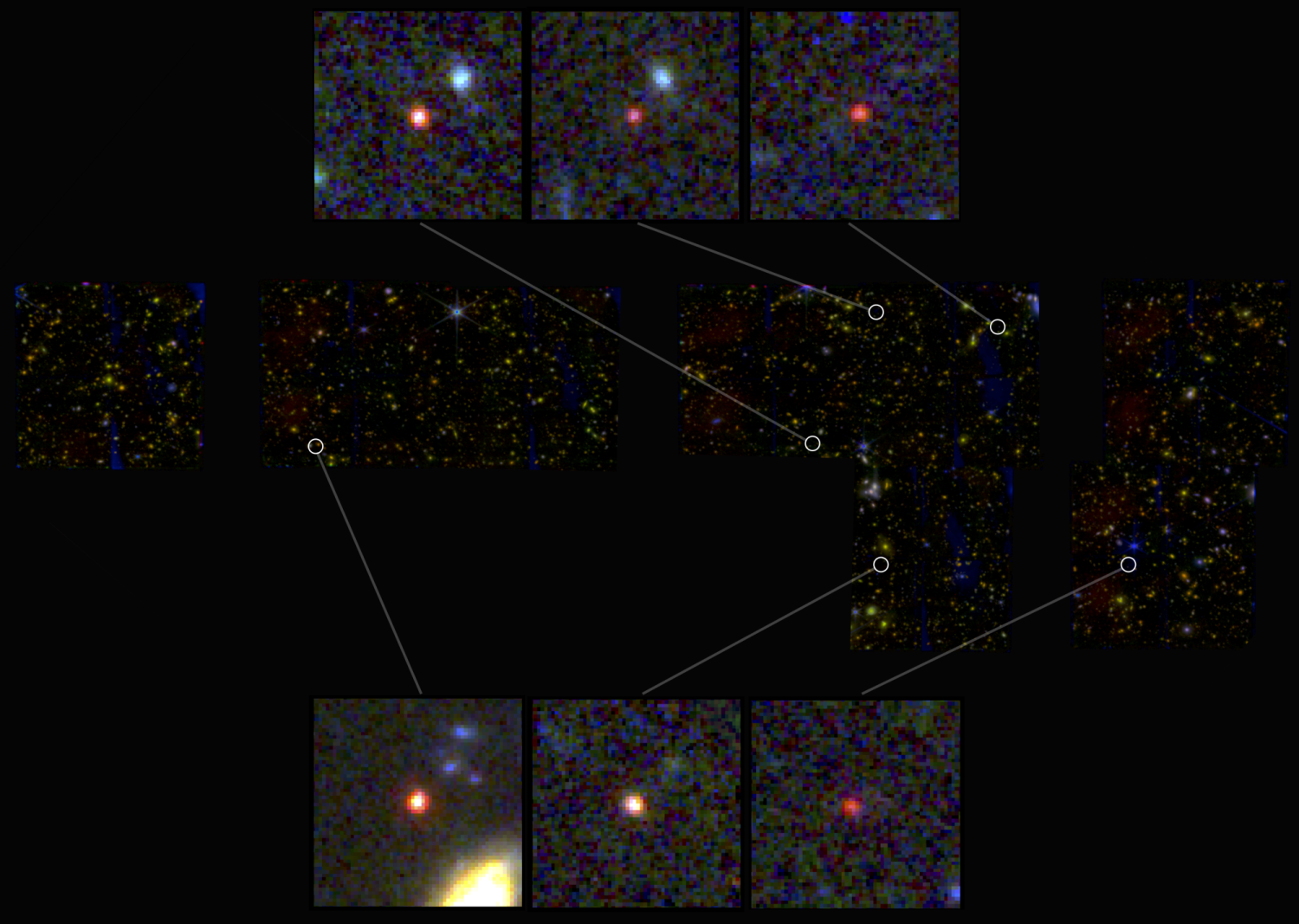
Webb’s images show several faint but very bright points of light, which the instruments flagged in red, indicating they are very old.
“We took our first look into the very early universe and had no idea what we were going to find. And they saw something so unexpected that it really creates problems for science. This calls into question the whole picture of early galaxy formation,” said Joel Leia, one of the authors of the study.
Previously, James Webb recorded even older galaxies that formed about 350 million years after the Big Bang. But they are tiny and did not negate our knowledge of astrophysics.
The age and size of these six galaxies suggest that they formed hundreds of stars every year after the Big Bang. (By comparison, the Milky Way forms only one or two new stars each year). In addition, these potential galaxies are about 30 times more compact than our own.
Scientists admit that there is a possibility that the fuzzy red dots they saw are something else, such as faint quasars or supermassive black holes. Objects may also not correspond to the projected dimensions. The team of scientists will later obtain additional data and verify their findings using spectroscopy. Therefore, official confirmation is expected no earlier than next year.
Source: Engadget