Partner of the Military Tech chapter?

The U.S. Air Force, along with Boeing, has autonomous technology, and a demonstration on a C-5 aircraft demonstrated the promise of using drones to assist in aircraft maintenance. But now the defense giant needs to overcome its “biggest limitation” — making sure the drones actually work in all weather conditions.
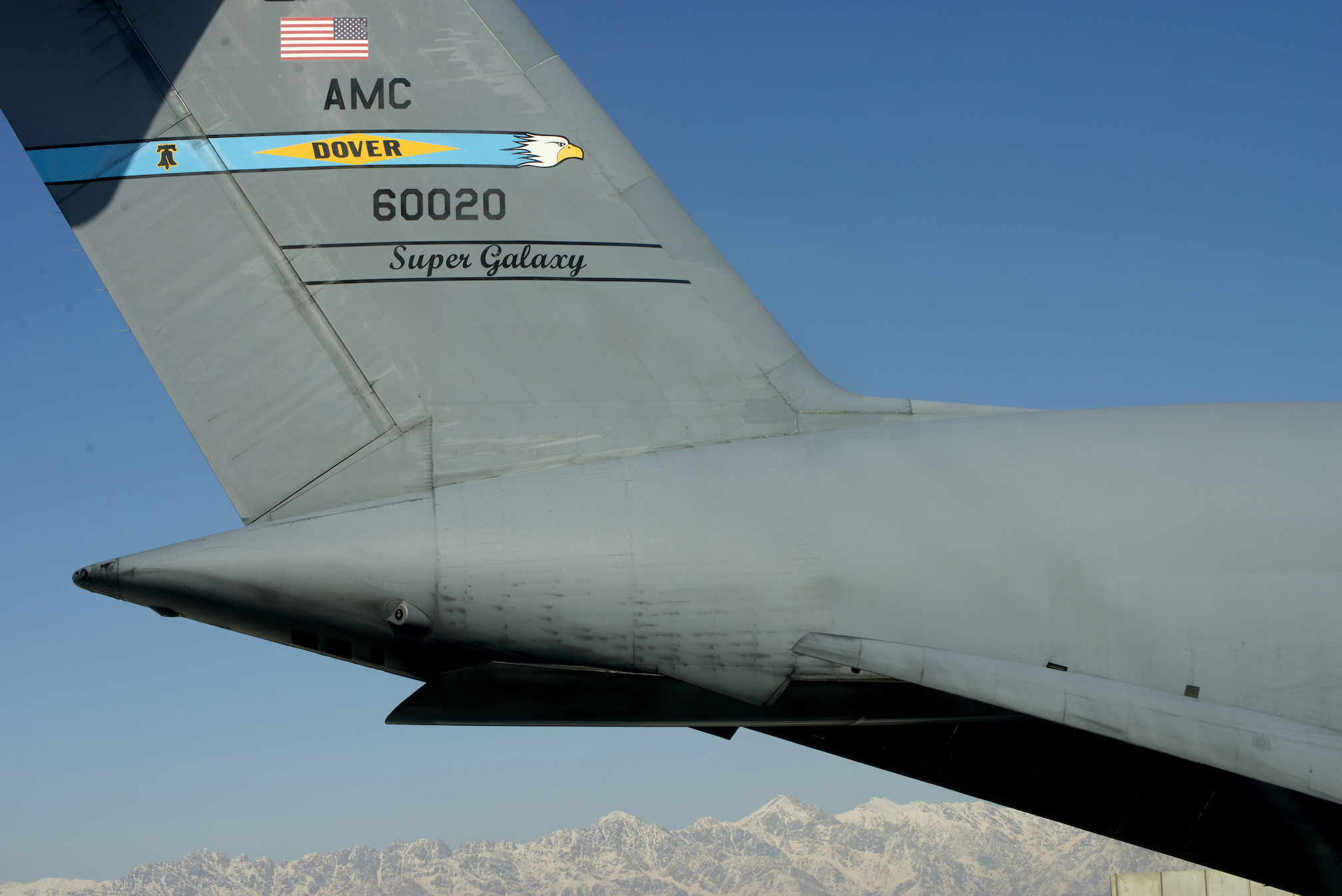
During a recent demonstration in a hangar at Dover Air Force Base, Delaware, the drone worked its way around the quarter of a C-5, pausing and hovering over various parts of the plane, taking pictures that were instantly transmitted to a ground control station, Breaking Defense reported.
The demonstration was part of Boeing’s Aircraft Autonomous Inspection (AAI) program, a joint program launched several years ago with autonomous aviation company Near Earth Autonomy. Two companies conducted the first drone scan of a C-5 aircraft to help with maintenance in a hangar at Dover Air Force Base.
David Murphy, a senior test pilot for the Near Earth Autonomy program, told reporters that the “vast majority of the benefit” of the program will be outside the hangar, where aircraft can be scanned right on the runway.
Representatives from Boeing, Near Earth Autonomy and the Air Force watched as the drone passed through 34 seats on the plane, stopped and hovered over the plane’s wing, next to the left side of the plane’s door and 20m above its tail.
It’s what Scott Belanger, the head of Boeing Global Services, called the “crescendo moment,” a process that usually involves multiple inspectors wearing safety belts with yellow ropes stretched along the plane, unable to see beyond the tail of what the drone is capable of. According to Belanger, it usually “takes a crew an hour and a half just to get up there.”
After completing the inspection, the drone slowly returned to the ground, spending just 10-15 minutes scanning a quarter of the 75-meter plane—much less time than a human safety inspection would take, and more accurate. The 34 inspection points that the drone had to pass were determined based on a plan created using a 3D model of the aircraft, taking into account the requirements of the US Air Force.
Partner of the Military Tech chapter?

Brave Inventors is a national platform of inventors and wartime inventions. Here you can place your military inventions, talk about developments and prototypes, find the necessary funding or a mentor, and also get more opportunities to cooperate with manufacturers, enterprises and businesses. You can support inventions by following the link.