Passport characteristics, scope of delivery and price
| Kinematic system | two driving wheels |
|---|---|
| Cleaning method | wet wiping with water supply to reusable wipes |
| Cleaning modes | automatic, along walls, local, intensive, Y-motion, manual control, 50-minute cleaning |
| Obstacle sensors | IR sensors for proximity, height difference, obstacles from above |
| Body control | mechanical button |
| Remote control | IR remote control |
| Alert | LED indication, sound signals |
| Battery Life | cleaning cycle 50 minutes, maximum 100 minutes total |
| Charging time | 100 minutes, 150 minutes after full discharge |
| Noise level | 46 dB |
| Travel speed | about 0.2 m/s |
| Power | 27 W |
| Charging method | from an external power adapter |
| Autonomous power supply | lithium-ion battery, 11.1 V, 23.87 Wh, 2150 mAh |
| Weight | 1.5 kg |
| Dimensions | 327(W)×165(D)×136(H) mm |
| Contents of delivery |
|
| Description on the site | Everybot Edge |
| Price in the company’s online store at the time of publication of the article | 18 900 rubles |
| Retail offers |
Appearance and function
The robot and everything to it is packed in a not very large, modestly decorated corrugated cardboard box.

The contents of the box are protected by foam inserts. The plastic handle on top makes it easy to transport the purchase. The package contains everything you need to start using the robot immediately after charging (the instruction manual was not accidentally in the box, but it was sent to us in the form of a PDF file).
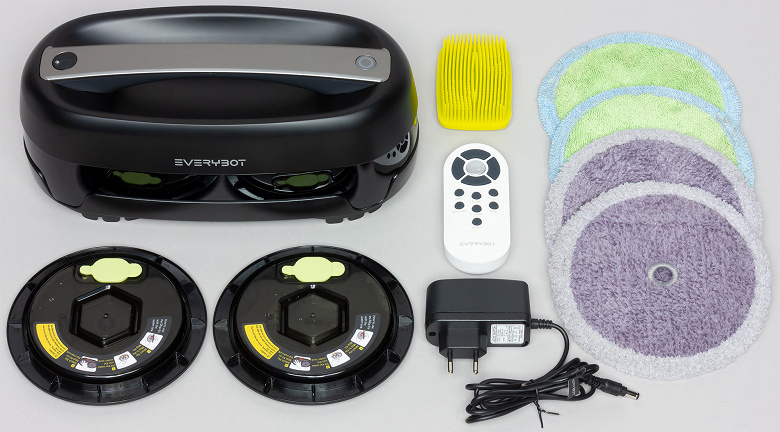

The robot is a continuation of Everybot’s line of automatic floor polishers – RS500 and RS700 . The new Everybot Edge robot is slightly smaller and lighter than the previous ones and, most importantly, it does not have mechanical bumpers; now obstacles are detected only with the help of infrared proximity sensors.
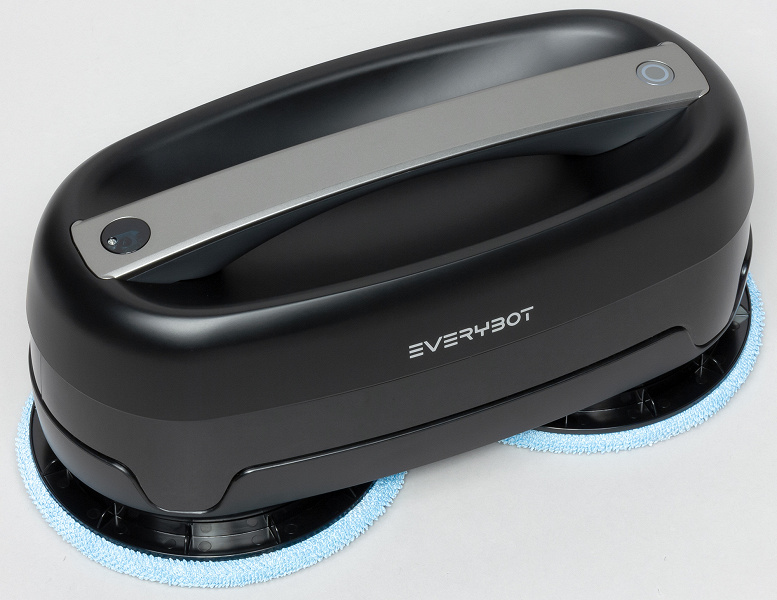

According to our measurements, the height of the Everybot Edge when loaded is 136mm.

Compared to the height of a typical robot vacuum, this is relatively large, potentially reducing the floor area available to the robot. The body length is 305 mm and the width is 151.5 mm. Cleaning wipes protrude slightly beyond the dimensions of the case, which, according to the manufacturer, improves the quality of cleaning close to obstacles.
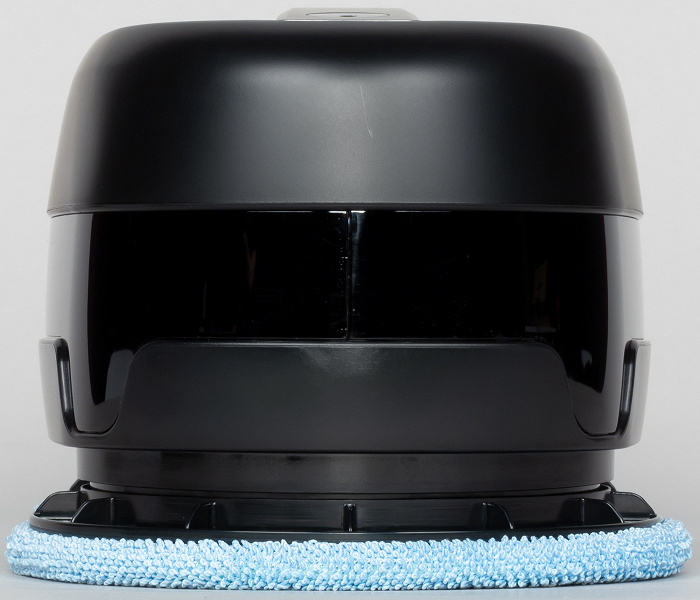

The robot weighs 1562 g without taking into account the filled water. The body of the robot is mainly made of black plastic with a matte finish. The jumper on top forms a handle for which the robot is conveniently carried, and for which the user holds it in manual cleaning mode. The bottom of the handle is dark gray, while the top has a silver finish that is relatively easy to damage. The perimeter of the robot is surrounded by wide inserts made of transparent tinted plastic with a mirror-smooth surface, behind which are placed IR sensors for obstacles and height differences.

On the handle on the left (before – this is where Everybot is written) there is a mechanical button to start and stop cleaning, which is also a status indicator. The button is made of milky white translucent plastic and has a silver finish. The button ring is left uncoated. The button, depending on the state of the robot, is highlighted in blue, yellow or red. During charging, the button flashes yellow once every two seconds, when the battery is fully charged, the backlight of the button goes out. This is a very inconvenient way of indicating, since you need to look at the robot for a long time to determine its state, and the end of charging cannot be distinguished from the state when, for some reason, external power is not supplied. During normal operation, the button is highlighted in blue, just before the end of work due to the discharge of the battery, the button is highlighted in yellow. For fixable problems that occur during cleaning, the button flashes amber. Flashing red indicates a power problem or something more serious. In addition, the robot informs about some changes in the state with the help of low-profile sound signals (start and stop cleaning, end of charging, error). On top, on the end of the handle opposite the button, there is an optical sensor, consisting of an IR diode and an IR receiver. Using this sensor, the robot determines if it is under the furniture at the moment when the cleaning is completed, and if so, the robot tries to get out into the open space so that it is easier for the user to detect the robot. The IR receiver apparently also receives signals from the remote control.

At the bottom in the back there is a connector for charging the battery work.

The length of the external power adapter cable is 1.4 m. The battery is located under the cover on the bottom. The battery is made up of three elements of the 18650 form factor.

On the bottom there is a battery compartment cover with a sticker and two disks. The discs are electrically driven and can rotate independently of each other. Round pads for wiping wipes are attached to these disks (in the photo below, on the left, the pad is installed on the disk, on the right, there is no pad).

Wiping wipes themselves are fixed on the Velcro pads.

The axes of the drives are slightly inclined relative to the perpendicular to the bottom so that the edges of the disks in the center of the robot are slightly raised relative to the floor, therefore, in working condition, the robot presses the edges of the napkins more strongly on the right and left relative to the body. As a result, when the disks rotate in the opposite direction with equal speed, the robot moves in a straight line forward or backward. At least this rule is carried out on a fairly even flat floor, and if the grip of the discs with the floor is the same. If the disks rotate in the same direction at the same speed, then the robot rotates in place. If the disk rotation speeds are different, then the robot moves in an arc. Sideways (with the narrow part of the body forward), the robot cannot move. The pads are 148 mm in diameter and the napkins are approximately 165 mm in diameter.
Before cleaning, wipes should be well moistened with water and squeezed out, and then fixed on the platforms so that the central hole in the towel is aligned with the protrusion in the center of the platform. To keep the wipes moist, you need to pour water into the containers on the platforms, and close the filling holes with plugs made of elastic plastic. These containers hold 66 ml of water. Note that it is necessary to fill in clean water.

Water enters the napkin through a hole in the platform closed with fibrous material.

At the end of cleaning, you need to remove the pads with napkins, pour out the remaining water from the tanks, leave the pads to dry with open plugs, and wash and dry the napkins. The manufacturer recommends washing the pads in soapy water using a special brush included in the package. In our experience, wipes can also be washed in a washing machine at 40 degrees, wring out and dry at normal temperature.
Napkins are made using microfiber. They are relatively thick and can hold a significant amount of liquid. The top absorbent layer is fibrous. The bottom surface of the napkins is different. For greens, it’s just microfiber terry cloth.
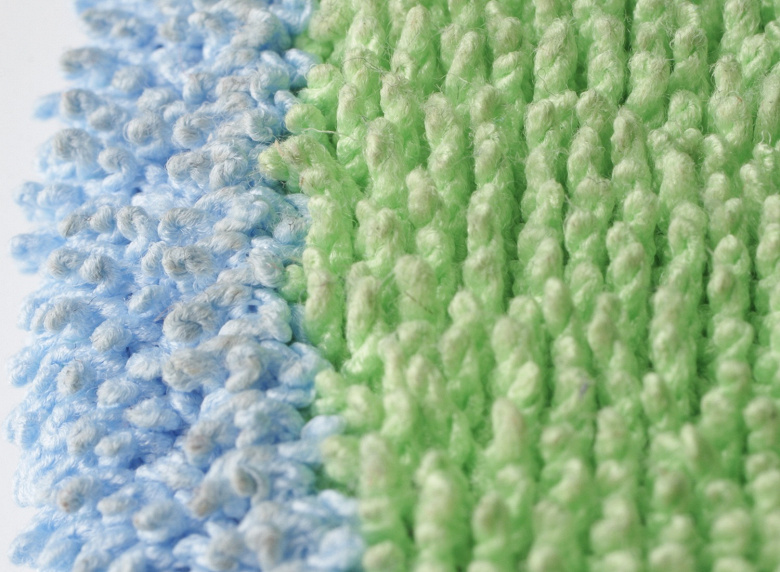

These wipes are recommended for use on smooth floors.
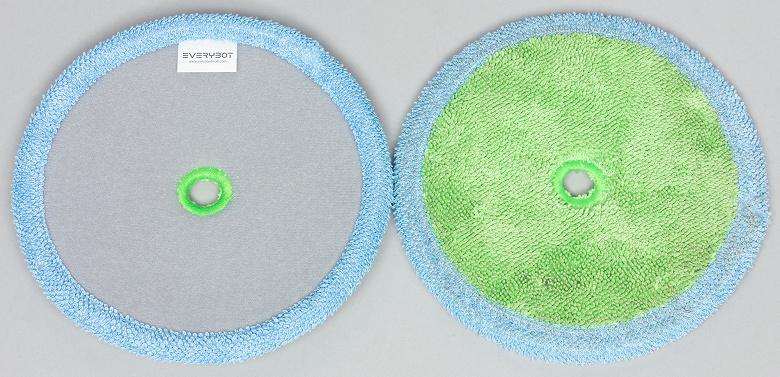
Gray wipes have a soft fringe at the bottom with bristles that help scrape dirt out of small depressions.
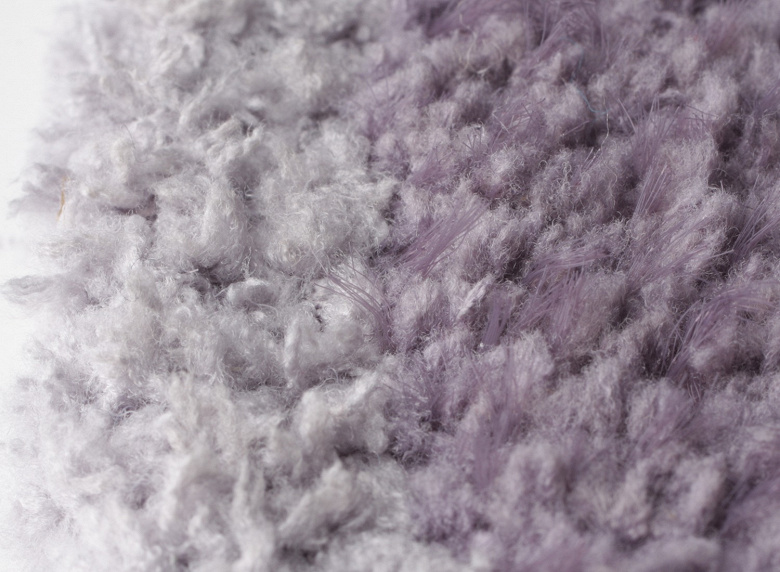

These wipes will work better on uneven floors such as tiled floors.

The perimeter of both types of napkins is edged with microfiber terrycloth.


The robot comes with a small IR remote control. Its body is plastic, white and matte on the outside. Most of the buttons are made of rubber-like material, with only the center button being hard plastic with a silver finish. The remote control is comfortable in the hand.

The main cleaning mode is automatic. In this mode, the robot independently goes through several motion options. The automatic mode is started either by the button on the robot body, or by the start / stop button on the remote control, or by the Auto button on the remote control. Only from the remote control, the user can turn on the local cleaning mode (Focus button), make the robot move only along walls and other obstacles (Edge), select a Y-shaped trajectory of movement (Y-mode), start the intensive cleaning mode (Intensive), turn on the restriction on 50 minutes of operation (there is enough water in the tanks for about this time; button 50min) and turn off the height difference sensors. The latter can be useful if the robot cleans floors with very dark areas. In addition, the forward/backward and right/left buttons can be used to manually control the movement of the robot. Also, the robot can be used in manual mode, holding it in your hands and pressing it against the surface to be cleaned. Manual mode is activated by double pressing the button on the body of the robot when the robot is held in the air. The robot is not very heavy, so the hand will not get tired quickly when cleaning vertical surfaces. The robot was made in Korea. The manufacturing company has an official representative office in Russia, there are also official service centers in the regions of Russia .
Testing
The testing of this floor cleaning robot was somewhat superficial, as we have neither the appropriate technique nor the room suitable for serious tests. As a test, we launched the robot in several rooms with linoleum on the floor. The robot does not orient itself in space and does not build a map; its movement is conditionally random. The robot circles the black rug, apparently focusing on the floor lift sensors. The robot can avoid touching high bright obstacles by detecting their presence with IR sensors. The collision of the robot with something on the floor, as a rule, does not occur at high speed, there is little noise from this and the robot almost instantly drives off the obstacle and changes direction. It is better to use the robot on fairly flat floors, since the robot can perceive areas with even a small height difference as an obstacle that needs to be bypassed. The robot does not overcome any thresholds; at best, it can pass through the joint of the floor covering, closed by a flat low bar. In general, the robot cleans well in those places where there are a lot of obstacles on the floor, although once it could not get out from under a chair, the distance between the legs of which is slightly larger than the length of the robot’s body, while getting under the chair and getting out from under it It was only possible on one side of the four. In the cleaning mode along the walls, the robot moves almost close to the wall, grabbing the bottom of the baseboard with a napkin. It seemed to us that in the automatic mode the robot does not clean very carefully close to the walls, so it is better to manually turn on the wall-following mode for some time during cleaning. Moisture is moderate, after a few minutes the trail of the robot is already dry (but the humidity in the room was rather low), so the robot can be used to clean all types of smooth floors, including non-moisture resistant laminate, parquet and plank floors. In our conditions, the water in the tanks ran out at about the 50th minute of operation, while most of the time the wet track went in two lanes with a dry gap in the center. Recall that with the help of an optical sensor, the robot determines the presence of an obstacle from above, and if it is under the furniture at the end of the cleaning cycle (with a time limit or until the battery is almost completely discharged), then it tries to get out into the open space to make it easier for the user to find it . On a single battery charge, the robot worked for 1 hour 55 minutes. The napkins look like this:

A lot of dirt is washed off napkins, and napkins also collect small debris, hair, threads, etc. well. However, it is better to pre-clean the floor of debris, for example, using a robot vacuum cleaner. Hand-washing wipes is not easy, but washing in the washing machine gives them a near-original look.
The robot charges relatively quickly, in our tests in 1 hour 17 minutes. During charging, the consumption from the socket reaches about 16.5 W, the robot charged and connected to the network consumes about 2.2 W, and the adapter not connected to the robot consumes about 0.16 W.
The robot is relatively quiet. From a distance of about 1.2 m above the robot, our measurements showed that during the phase of fast rectilinear movement, the noise level reaches 54 dBA, when the robot slows down, it decreases to 50 dBA. For comparison, the noise level in these conditions of a conventional (not the quietest) vacuum cleaner is approximately 76.5 dBA.
findings
Considering the absorbency of the wipes, their working surface, the rotation and pressing of the wipes to the floor, and the good wetting of the floor, you should expect this robot to cope well with wet cleaning of the floor. Cleaning in manual mode has become more convenient, as compared to previous models, the weight of this robot has decreased. Everybot Edge has a reduced body size, which can potentially improve the quality of cleaning close to obstacles. The robot does not have movable bumpers, which also potentially increases reliability. In addition, the new model is much quieter than the previous one. One can only regret that now the charging base is missing even as an option.
In conclusion, we suggest watching our video review of the Everybot Edge robot floor polisher:
You can also watch our video review of the Everybot Edge robot floor polisher at iXBT.video