Passport characteristics, scope of delivery and price
| Manufacturer | MSI |
|---|---|
| Model | MEG CoreLiquid S360 |
| Type of cooling system | liquid closed type pre-filled non-expandable for processor |
| TDP | there is no data |
| Compatibility | motherboards with processor sockets: Intel: 1150/1151/1155/1156/1200/1700 , 2011/ 2011-3 /2066; AMD: AM4/FM2+/FM2/FM1/AM3+/AM3/AM2+/AM2 and TR4/sTRX4/SP3* * the frame is included with the processor |
| Fan type | axial (axial), MEG Silent Gale P12 (PLA12025S12H-4), 3 pcs. |
| Fan power | 12 V, 0.36 A, 4-pin connector (common, power, rotation sensor, PWM control), 350 mm cable |
| Fan dimensions | 120×120×25 mm |
| Fan speed | 0-2000 rpm |
| Fan performance | 95.5 m³/h (56.2 ft³/min) |
| Fan static pressure | 21.7 Pa (2.21 mm w.c.) |
| Fan noise level | 22.7 dBA |
| Fan bearing | hydrodynamic bearing (Hydro-Dynamic Bearing) |
| Fan life | 50 000 h |
| Radiator dimensions | 394×120×27mm |
| Radiator material | aluminum |
| Hose length | 400 mm |
| Hose material | plastic (PVC) braided |
| water pump | integrated with a heat sink, equipped with a fan to cool the VRM |
| Pump power | 0.33 A, 4 W, connected to the SATA power connector from the PSU (general, power supply 12, 5 and 3.3 V) |
| Pump rotation speed | 2800 rpm |
| Pump noise level | 21.2 dBA |
| Water block dimensions | 95×95×54 mm |
| Heat sink material | copper |
| Heat sink thermal interface | applied thermal paste |
| Pump life | 50 000 h |
| Connection |
|
| Peculiarities |
|
| Contents of delivery |
|
Description
The liquid cooling system is delivered in a stylishly designed corrugated cardboard box. There is color printing, gold foil stamping and varnished areas – the manufacturer did not save on the design of the box. On the outer planes of the box, not only the product itself is depicted, but also some features are listed (with text and pictures), as well as technical specifications. The inscriptions are mostly in English, but the link to the site for more information is duplicated in several languages, including Russian. To protect and distribute parts, a papier-mâché mold, polyethylene foam padding, a thin cardboard radiator cover and plastic bags are used. The sole of the heat sink is protected by a casing made of hard plastic, and the screen and sight glass on the pump are protected by a plastic film.

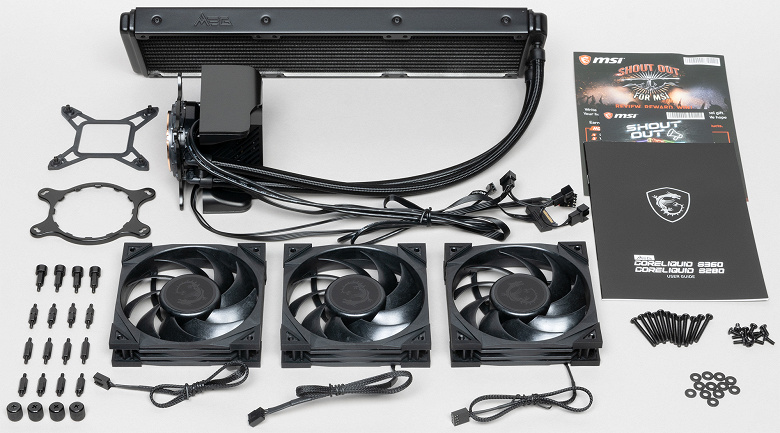
Inside there is a radiator with a connected water block, fans, a set of fasteners and installation instructions.

Instructions of good printing quality and with explanatory inscriptions in several languages, including Russian. It is mostly in pictures, so it is understandable without translation. The company’s website has a full description of the cooler and links to PDF files with instructions and technical data .
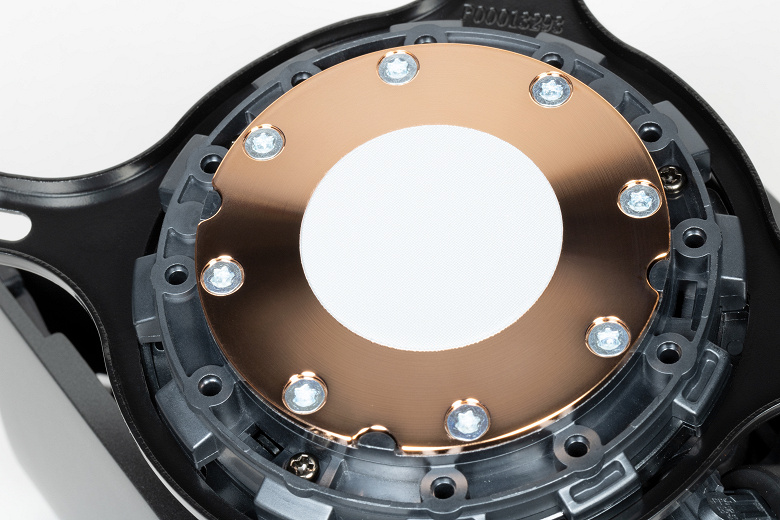
The system is sealed, primed, and ready to use. The pump is integrated into one unit with a heat sink. The sole of the heat sink, directly adjacent to the processor cover, is a copper plate 1.5 mm thick. Its outer surface is ground and slightly polished. Towards the center, the surface is convex with a difference of about 0.2 mm.
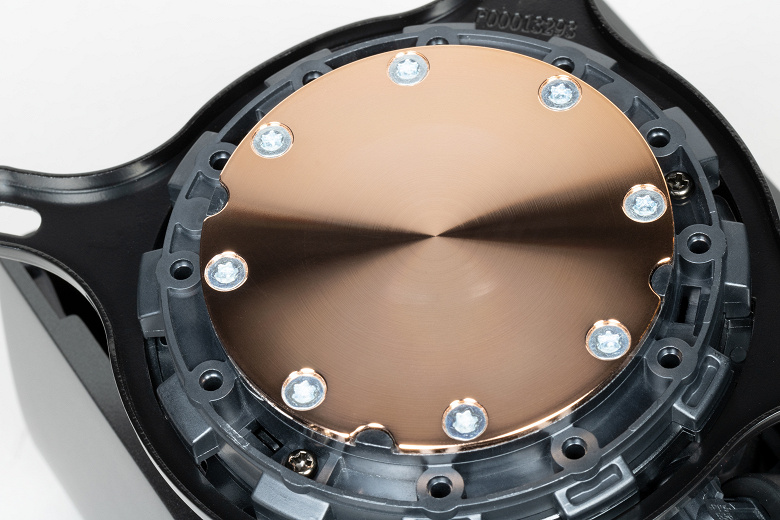

The outer diameter of this plate is 54.5 mm, and the diameter of the inner part, limited by holes, is 43.5 mm. The central part of the copper base is occupied by a thermal paste applied with a thin layer. Unfortunately, there is no stock for its restoration in the delivery set.

All tests used high-quality thermal paste from another manufacturer.
Looking ahead, we will demonstrate the distribution of thermal paste after all tests are completed. On an Intel Core i9-7980XE processor:
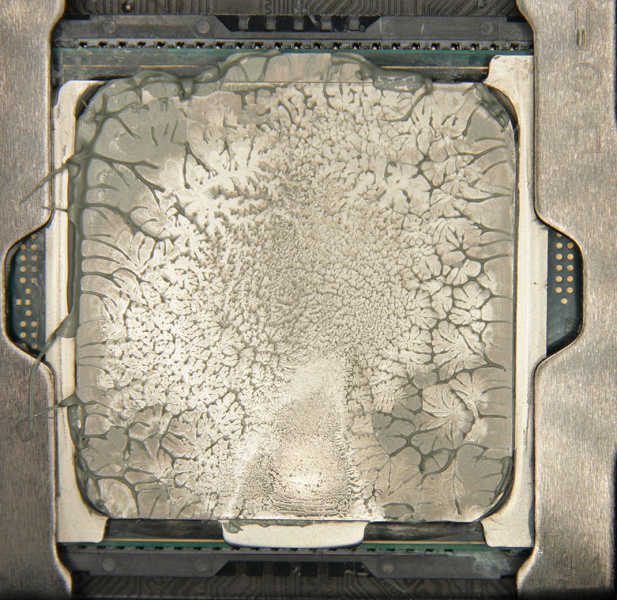

And on the sole of the water block:
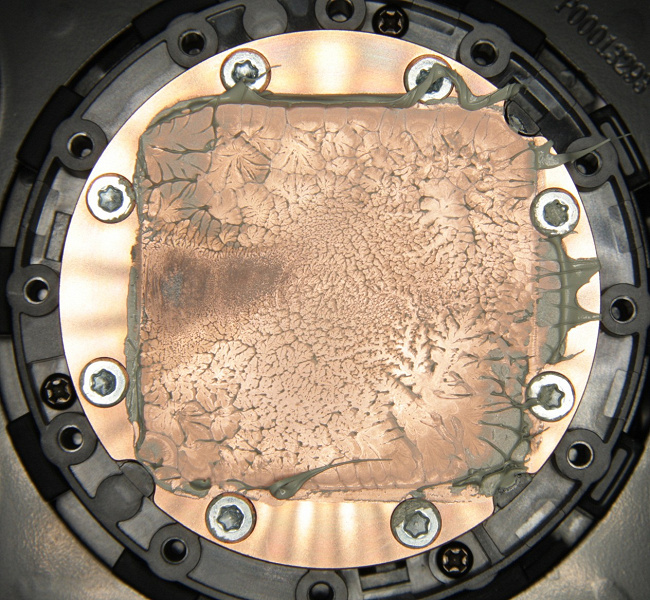
It can be seen that the thermal paste is distributed over the entire area of the processor cover, and approximately in the center there is a large area of u200bu200btight contact. Note that the cover of this processor itself is slightly convex towards the center.
And in the case of the AMD Ryzen 9 3950X processor. On processor:

On the sole of the heat sink:
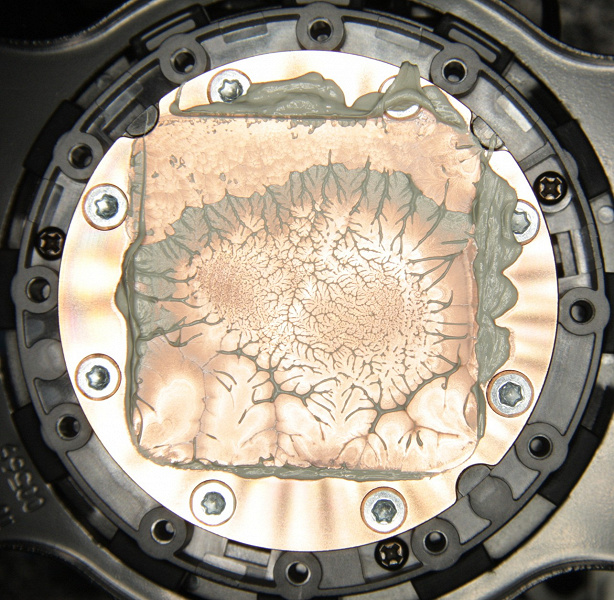
The situation is about the same. (The thermal paste distribution, of course, changed slightly when the processor and pump were separated.)
The body of the water block is made of hard black plastic.

First, the pump casing is fixed on top of the case, then the fan, then the monitoring and control board, and the LCD screen with its casing completes this sandwich. The surface of the screen itself is slightly matte, it is protected by a mineral glass plate between which and the screen there is an air gap. But that’s not all – a plastic casing is put on top of the pump, held in place by magnets. This casing has a mineral glass viewing window with a metallized surface, so it is a translucent mirror. This casing performs a decorative function, and also directs airflow from the fan to the right places. The design is completed by the extremely decorative aluminum alloy side plates with an anodized silver-dark gray semi-gloss finish. They are also fixed with magnets, for which there are magnets on the plastic casing, and steel plates are glued on the lining on the inside.

The hoses are encased in a slippery synthetic sheath. Outer diameter of braided hoses approx. 11 mm. The L-shaped fittings at the inlet to the pump rotate, which makes it easy to install the system.
The radiator is made of aluminum and has a relatively durable black matte finish on the outside.

The corners of the fan frame are covered with rubber pads. These elastic elements should theoretically reduce vibration noise, but in practice this will not happen, since the mass of the fan and the rigidity of the vibration damping elements make it possible to reasonably assume that, due to the high resonant frequency, this system will not have any significant effect anyway. anti-vibration properties.
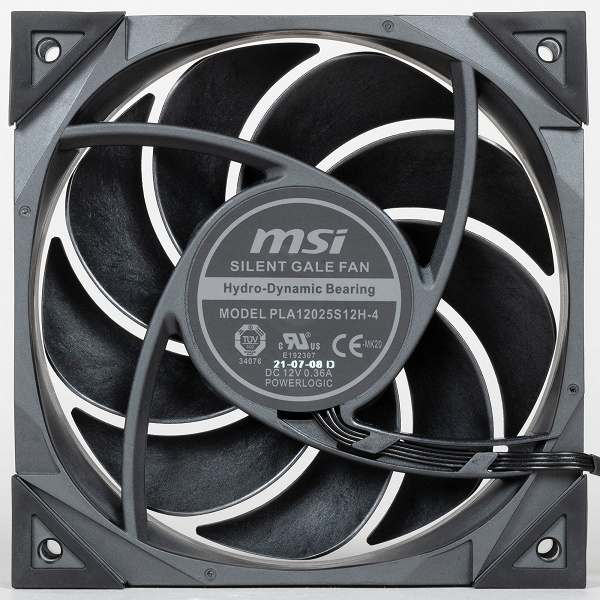

The fan has a four-pin connector (common, power, rotation sensor and PWM control) at the end of the power cable. This cable is encased in a slippery braided sheath. According to the legend, the sheath reduces aerodynamic drag, but taking into account the thickness of the flat three/four-wire cable inside this sheath and its outer diameter, we strongly doubt the veracity of this legend. However, the shell will allow you to maintain a single design style for the interior of the PC.
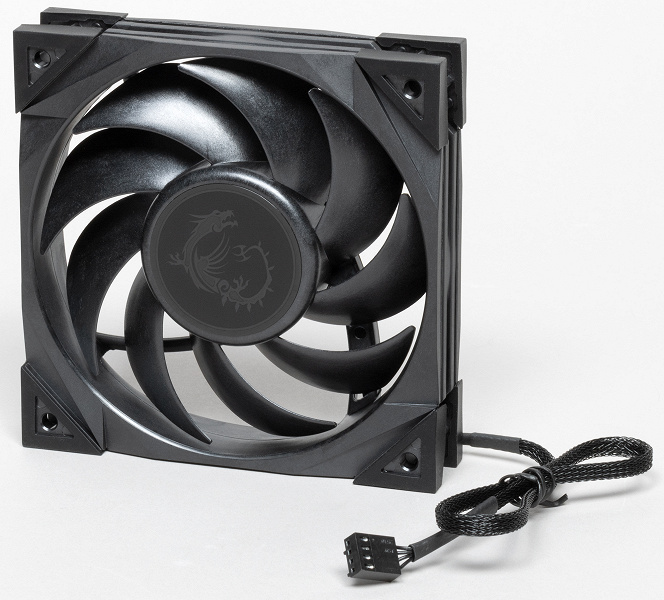

The fasteners are made mainly of hardened steel and have a durable black semi-gloss paint finish. The frame on the back side of the system board is made of durable plastic and equipped with steel threaded sockets in movable inserts. Compatibility with the Intel LGA 1700 connector is provided by special stands and the ability to adjust the pitch of the mounting holes. We note the convenient bayonet fastening of the pump frame, as well as large knurled nuts, which allows you to do without tools when installing the pump. The complete system with fasteners for LGA 2011 has a mass of 1604 g.
The pump features a built-in fan designed to cool the voltage regulator assembly (VRM) and other components surrounding the processor. There is an opinion that the use of LSS with conventional water blocks can reduce the stability of the system due to overheating of the VRM, since, unlike air coolers, these blocks are cooled worse if the LSS is installed. Of course, another fan contributes to increased noise levels and reduces the overall reliability of the system, but in a pinch it can be turned off.
Let’s do a practice test. First, let’s warm up the VRM well (the description of the load is below) to a constant temperature. Then we block the fan on the pump and, again waiting for a constant temperature, let’s see how much the temperature of the VRM heatsink rises.
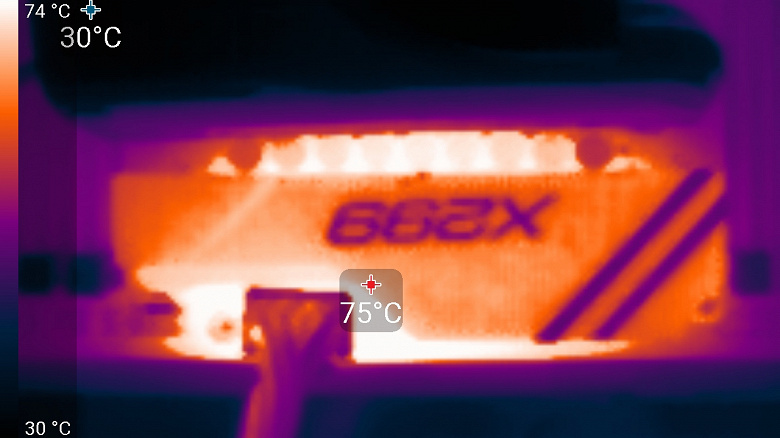
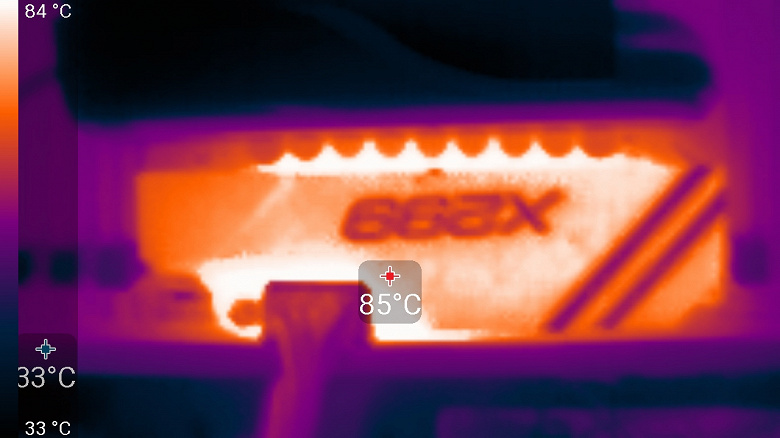


And for control, turn on the fan again:
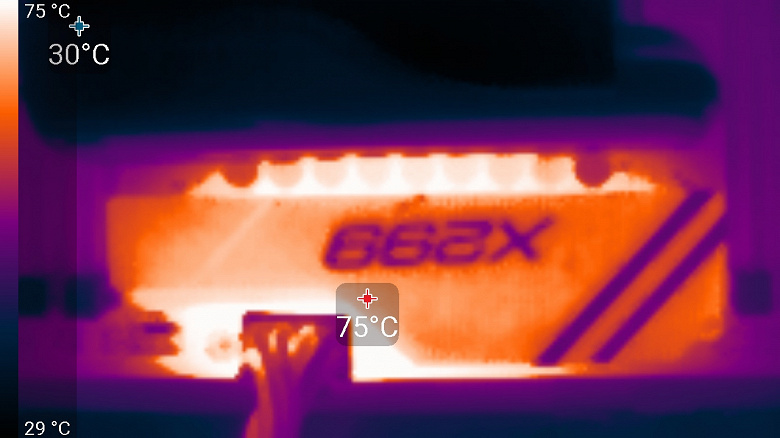

The temperature dropped again to the value in the first test. In this case, the effect is to lower the temperature by 10 degrees, which is very good.
Another feature of this LSS is the presence of an LCD screen. In order for the screen to be useful, the pump must be connected to the USB header on the motherboard (note that not everyone has this block), and MSI Center software must be installed on the PC. The functionality of this software, related to this system, is that the user can monitor the current fan speeds on the radiator and on the pump and the rotor of the pump itself, choose from the available (three profiles) or create your own fan and pump speed profiles, depending on on processor temperature.
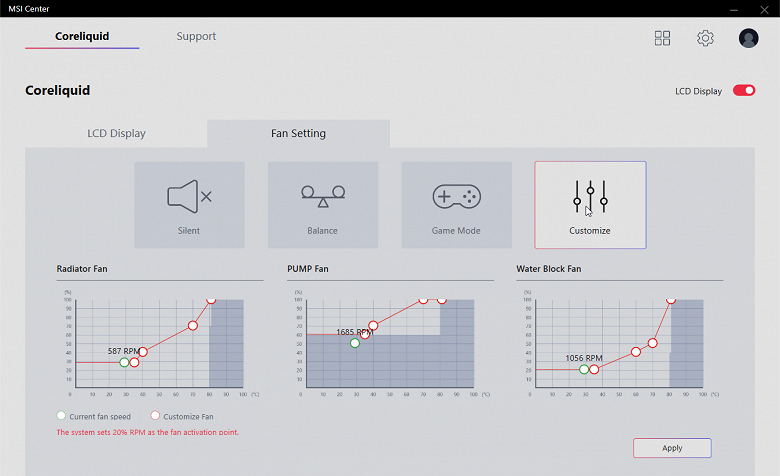
You can display temperature and rotation speeds from several sensors on the pump screen (cyclic change of readings):
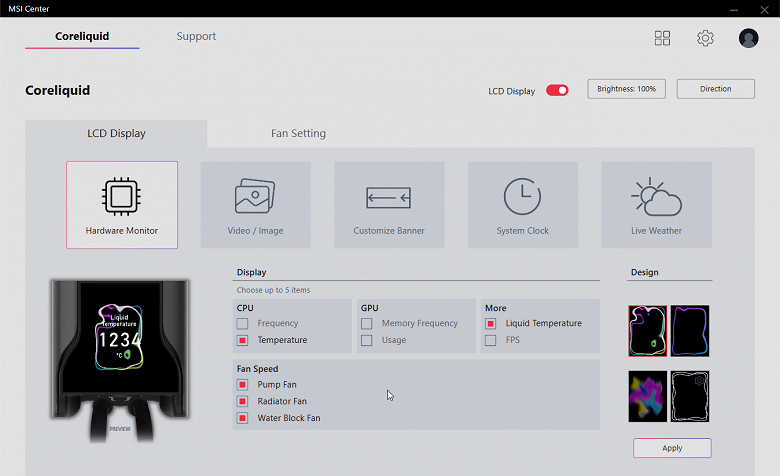
Static or dynamic splash screen.
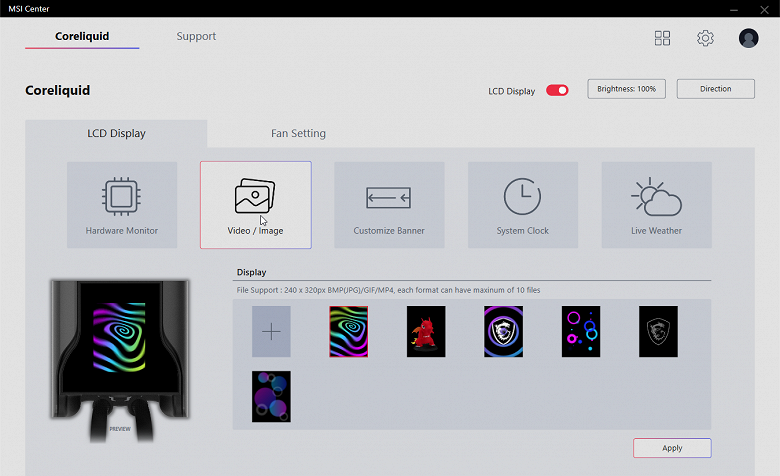
You can also set the background:
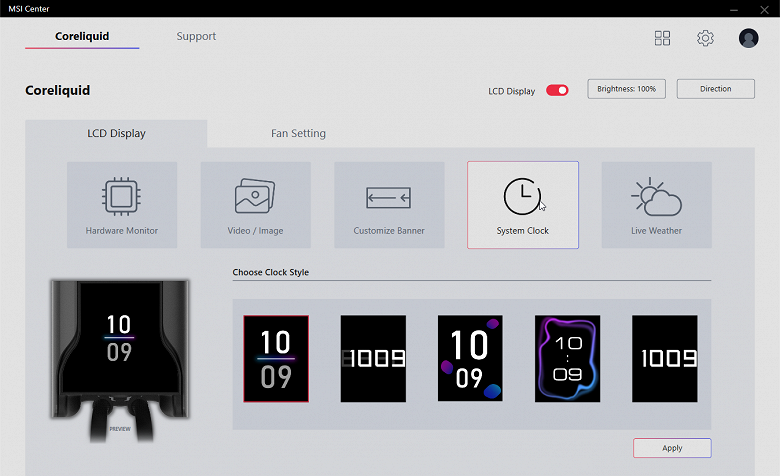
Display system frequency:
And weather data (it didn’t work for us):
Some display options, including an animated GIF, are shown in the video below:
Testing
A full description of the testing methodology is given in the corresponding article ” Testing methodology for processor coolers of the 2020 sample “. For the load test, the powerMax (AVX) program was used, all cores of the Intel Core i9-7980XE processor worked at a fixed frequency of 3.2 GHz (multiplier 32). In all tests, the pump was running at maximum speed.
Determination of the dependence of the cooler fan speed on the PWM duty cycle and / or supply voltage

The rotation speed adjustment range is very wide; Note that at a short circuit of 0% (more precisely, at 5% and below), the fans stop, which can be important in a hybrid cooling system with passive mode at minimum load. Fans are started at short circuit 10% and above.
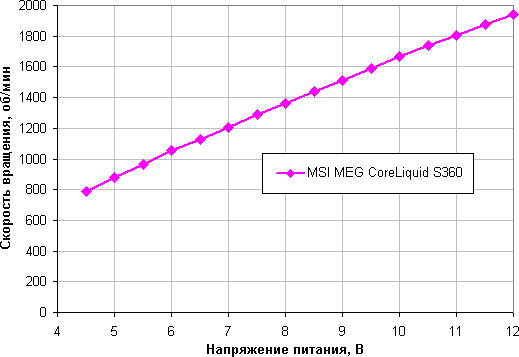
The change in rotation speed is also smooth, but the range of adjustment with voltage is much narrower. Fans stop at 4.2-4.3V and start at 4.3-4.4V. If necessary, it is permissible to connect them to 5 V. The rotation speed of the pump, as well as the fan on it, can be and can be adjusted bypassing the software, but it is definitely not easy. By default, if you do not use the software, then the pump and the fan on it operate at maximum speed.
Determination of the dependence of the temperature of the processor at its full load on the speed of rotation of the cooler fans

In this test, our 140W TDP processor is already overheating (at 24 degrees ambient) at fan speeds achieved with short circuit drops to 15% or less, but it’s only 300rpm or less.
Determining the noise level depending on the speed of rotation of the cooler fans
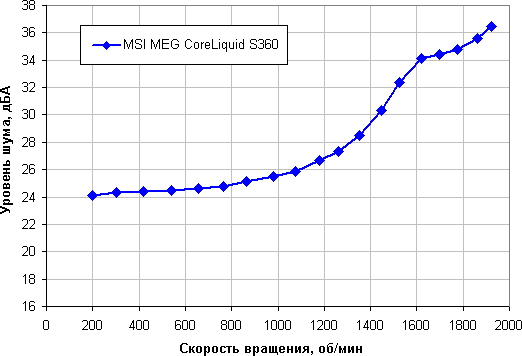
It depends, of course, on individual characteristics and other factors, but somewhere from 40 dBA and above, the noise is, from our point of view, very high for a desktop system; from 35 to 40 dBA, the noise level is classified as tolerable; below 35 dBA, the noise from the cooling system will not stand out much against the background of typical non-noisy PC components – case fans, fans on the power supply and on the video card, as well as hard drives; and somewhere below 25 dBA the cooler can be called conditionally silent. In this case, the noise from the LSS is not very high, even in the case of the maximum fan speed. The noise from the pump alone is 23.1 dBA. The pump is relatively quiet, but when the fan is turned on, the noise level rises to 29.5 dBA, which is high if the user wants to keep the noise level to a minimum. To the aid comes the adjustment of the speed of rotation of this fan with the help of software. In load tests, as well as when measuring the noise level, we turned off the fan on the pump completely. The background level was equal to 16.3 dBA (conditional value, which shows the sound level meter).
Plotting the dependence of the real maximum power on the noise level
Let’s try to get away from the conditions of the test bench to more realistic scenarios. Let’s say that the temperature of the air taken in by the cooling system fans can rise to 44 ° C (a realistic scenario when the fans on the radiator are set to blow out of the case in which the powerful video card is running), but the temperature of the processor under maximum load does not want to increase above 80 ° C. Restricting ourselves to these conditions, let’s plot the dependence of the real maximum power, denoted as P max (previously, we used the designation Max. TDP ), consumed by the processor, on the noise level ( details are described in the methodology ):
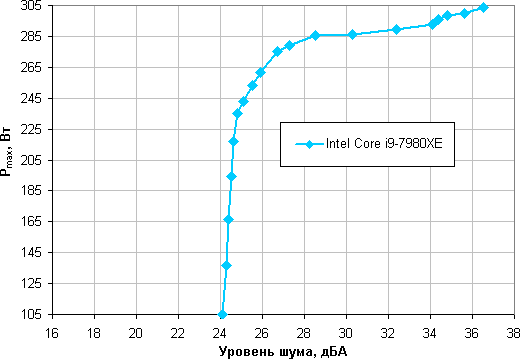
Taking 25 dBA as a conditional noiselessness criterion, we get the approximate maximum power of processors corresponding to this level, which is about 240 W. If you do not pay attention to the noise level, the power limits can be increased somewhere else up to 305 watts. Let us clarify once again that in harsh conditions of blowing the radiator with air heated to 44 degrees, when the air temperature drops, the indicated power limits for silent operation and maximum power increase. Note that the user can slightly reduce the noise level, while not greatly reducing the cooling capacity, if using the software to reduce the speed of the pump.
Comparison with other LSS when cooling the Intel Core i9-7980XE processor
Using this link , you can calculate the power limits for other boundary conditions (air temperature and maximum processor temperature) and compare this system with several other LSSs tested using the same methodology (the list is updated). As can be seen, the efficiency of this system in the high-power region among typical LSS with a radiator for three 120 mm fans is good, and in the low-power region it is not high, which is due to the relatively high level from the pump operating at maximum speed (which can be corrected – see Fig. note in the previous section).
Testing on an AMD Ryzen 9 3950X processor
As an additional test, we decided to see how this coolant will cope with the cooling of the AMD Ryzen 9 3950X . The processors of the Ryzen 9 family are assemblies of three crystals under one cover. On the one hand, increasing the area from which heat is removed can improve the cooling capacity of the cooler, but on the other hand, the design of most coolers is optimized for better cooling of the central area of the processor.
The dependence of the temperature of the processor at its full load on the speed of rotation of the fans:
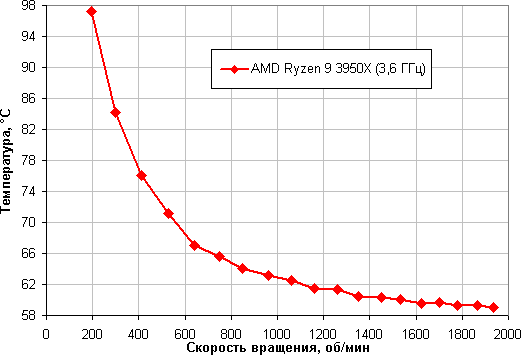
In fact, under test conditions, this processor overheats at 24 degrees of ambient air at a short circuit equal to 10%, which corresponds to only 190 rpm (for this CPU, heating up to 95 degrees is allowed).
Restricting ourselves to the above conditions, we plot the dependence of the real maximum power (denoted as P max ) consumed by the processor on the noise level:
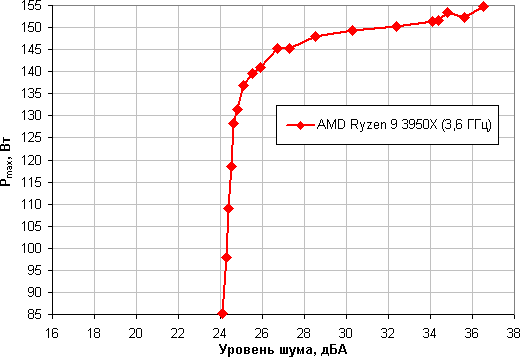
Taking 25 dBA as a conditional noiselessness criterion, we get that the maximum processor power corresponding to this level is about 135 W. If you do not pay attention to the noise level, then the power limit can be increased somewhere up to 155 watts. Once again, we will clarify: this is in harsh conditions of blowing the radiator with air heated to 44 degrees. As the air temperature drops, the specified power limits for quiet operation and maximum power increase. The result is noticeably worse than in the case of the Intel Core i9-7980XE processor. However, provided there is enough good ventilation in the case, this cooler will quite cope with the cooling of the AMD Ryzen 9 3950X processor, but you should not count on the possibility of significant overclocking.
Comparison with other coolers and coolers when cooling AMD Ryzen 9 3950X
You can use this link to calculate power limits for other boundary conditions (air temperature and maximum processor temperature). As you can see, the efficiency of this system in the high power region among typical LSS with a radiator for three 120 mm fans is excellent, and in the low power region it is again low, the reason for this and the way to combat it are described above.
findings
Based on the MSI MEG CoreLiquid S360 liquid cooling system, you can create a conditionally silent computer equipped with an Intel Core i9-7980XE (Intel LGA2066, Skylake-X (HCC)) processor with a heat dissipation of about 240 W maximum, and this is even taking into account the possible increase in temperature inside enclosures up to 44 °C and subject to long-term maximum load. In the case of the AMD Ryzen 9 3950X chiplet processor, the cooler efficiency is noticeably lower, and in order to comply with the above conditions, the maximum power consumed by the processor must not exceed 135 watts. With lower cooling air temperatures and/or less stringent noise requirements, the power limits can be increased. Also, the noise level can be reduced almost without consequences by moderately lowering the pump speed. The LCD screen on the pump can not only decorate the interior of the system unit, but also bring some benefit, helping the user to monitor the current PC settings and the weather outside the window. We note the good workmanship, convenient fastening of the water block, braiding of hoses and parts of cables, as well as a fan on the pump, designed to cool the VRM and other components surrounding the processor.
MSI’s MEG CoreLiquid S360 Liquid Cooling System wins the Original Design Editorial Award for looks and functionality.